Marfan Syndrome Diagnostic Criteria
Marfan syndrome diagnostic criteria. Frequent joint dislocations and subluxations partial dislocation often affecting the shoulder kneecap andor temporomandibular joint joint that connects the lower jaw to the skull. Pediatric Neurology features up-to-the-minute publication of the latest advances in the diagnosis management and treatment of pediatric neurologic disorders. Evaluation of the adolescent or adult with some features of Marfan syndrome.
The new diagnosis of hypermobility spectrum disorder HSD will include most people who have been previously diagnosed with joint hypermobility. 7 Mutations in regulatory sequences well outside the coding region will be missed by current methods used in clinical molecular diagnostic laboratories. Dean JA Blanchette VS Carcoa MD et al.
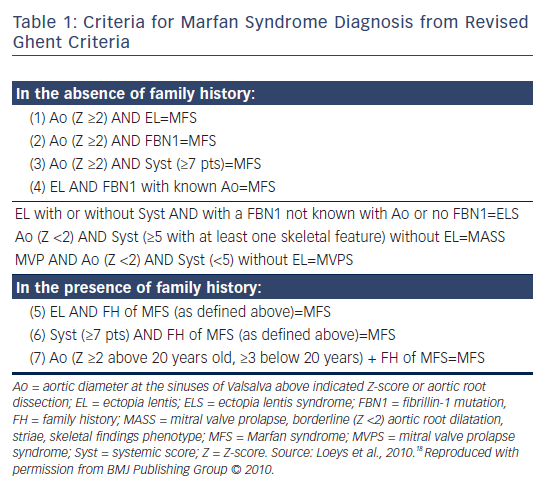
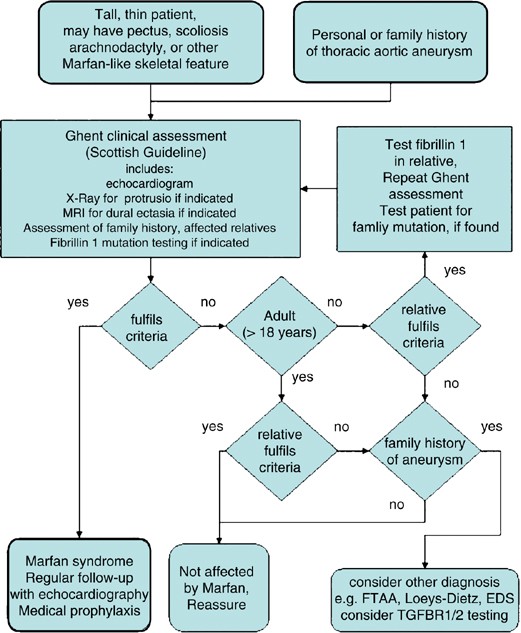
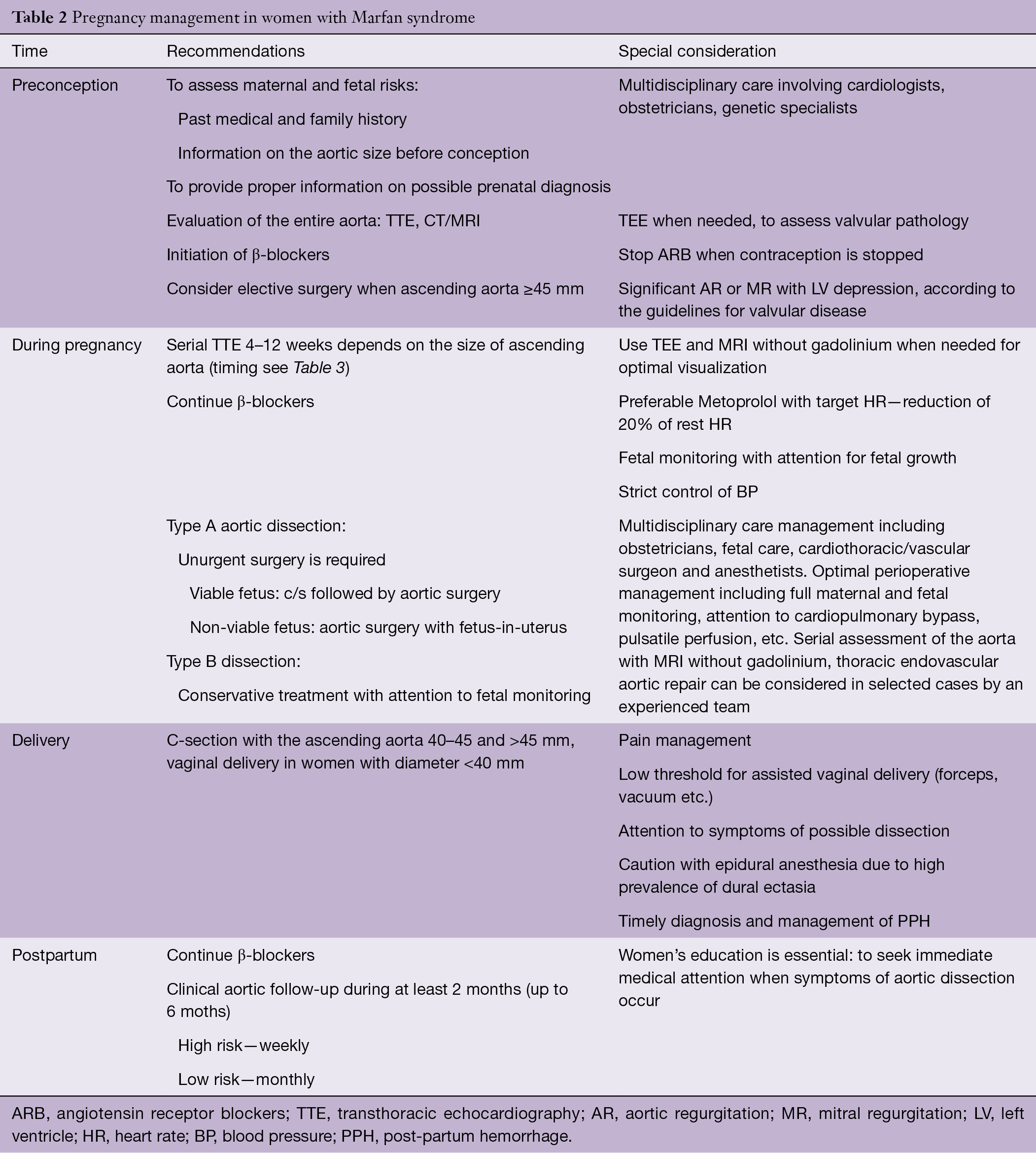
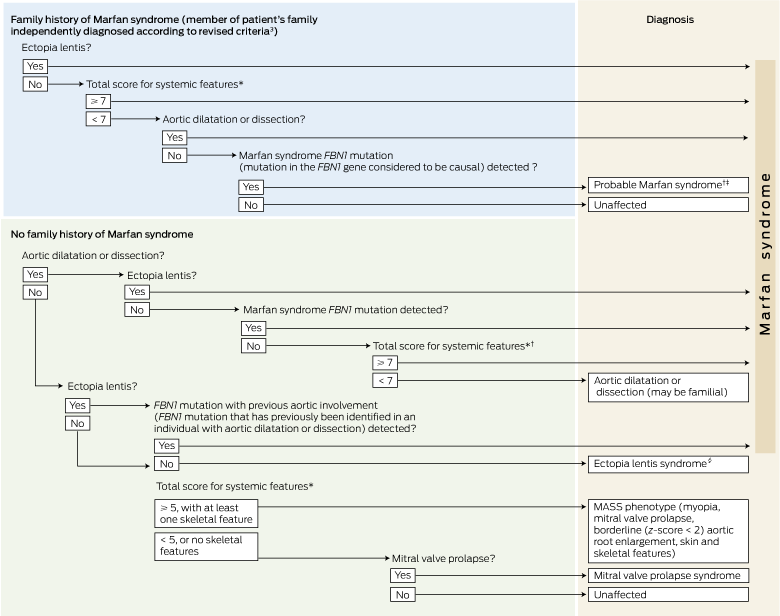
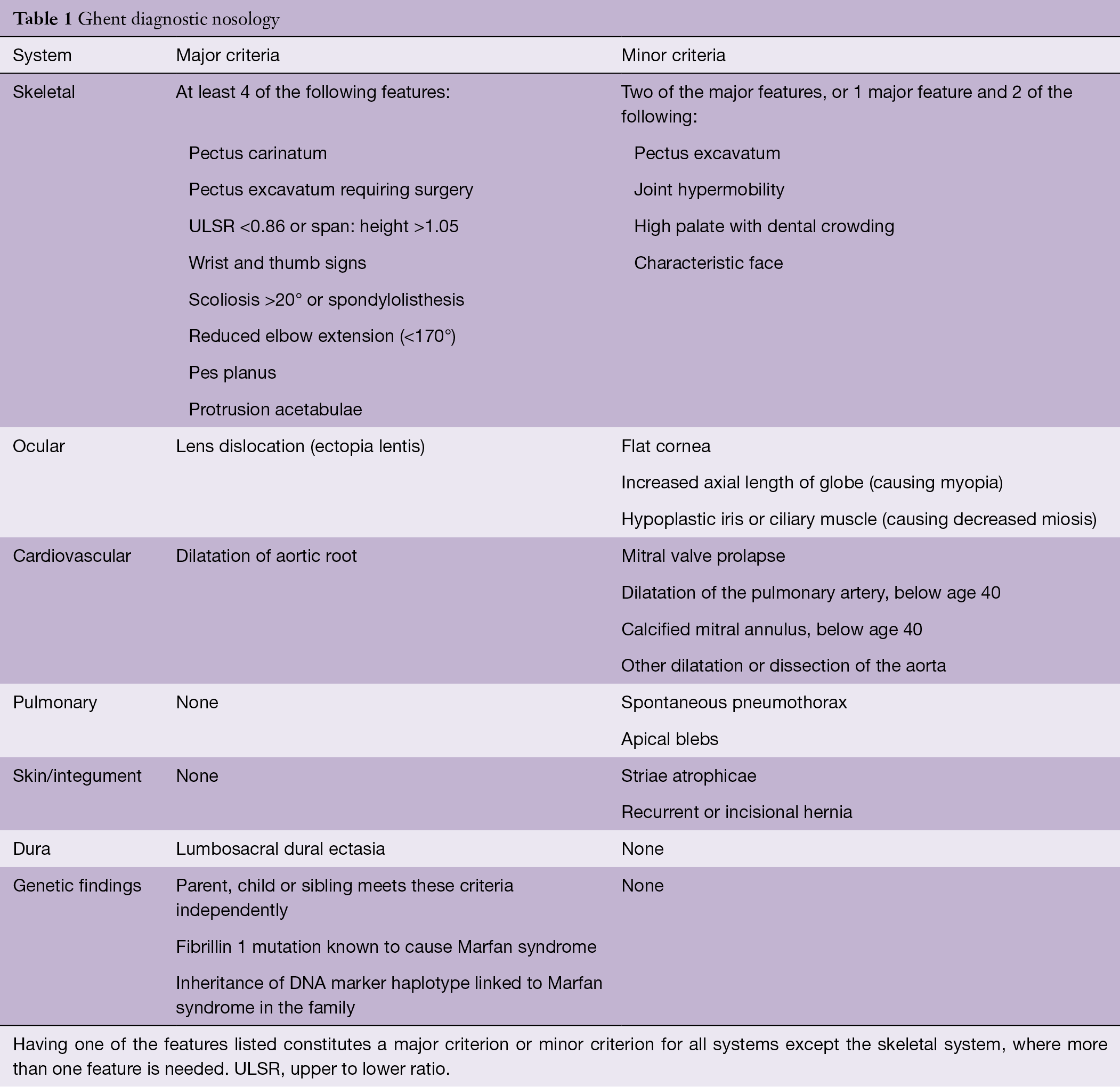
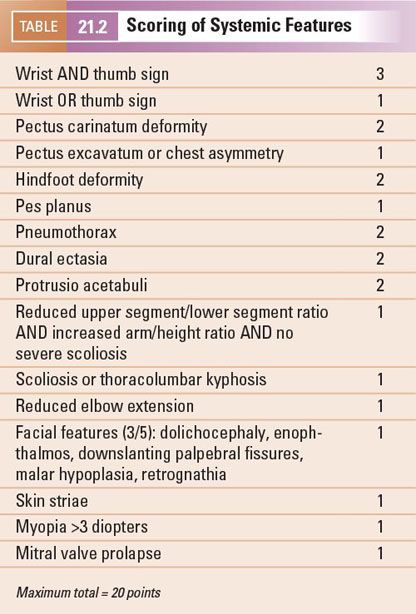
It was published in the Journal of Medical Genetics. Due to the widespread role of connective tissue throughout the body individuals with Marfan syndrome may be at risk for many potentially severe or lethal co-moribidities as a result of the disease process. The diagnosis of Marfan syndrome relies on a set of defined clinical criteria the Ghent nosology developed to facilitate accurate recognition of the syndrome and improve patient management and counselingTo decrease the risk of premature or missed diagnosis an international panel of experts revised the criteria in 2010.
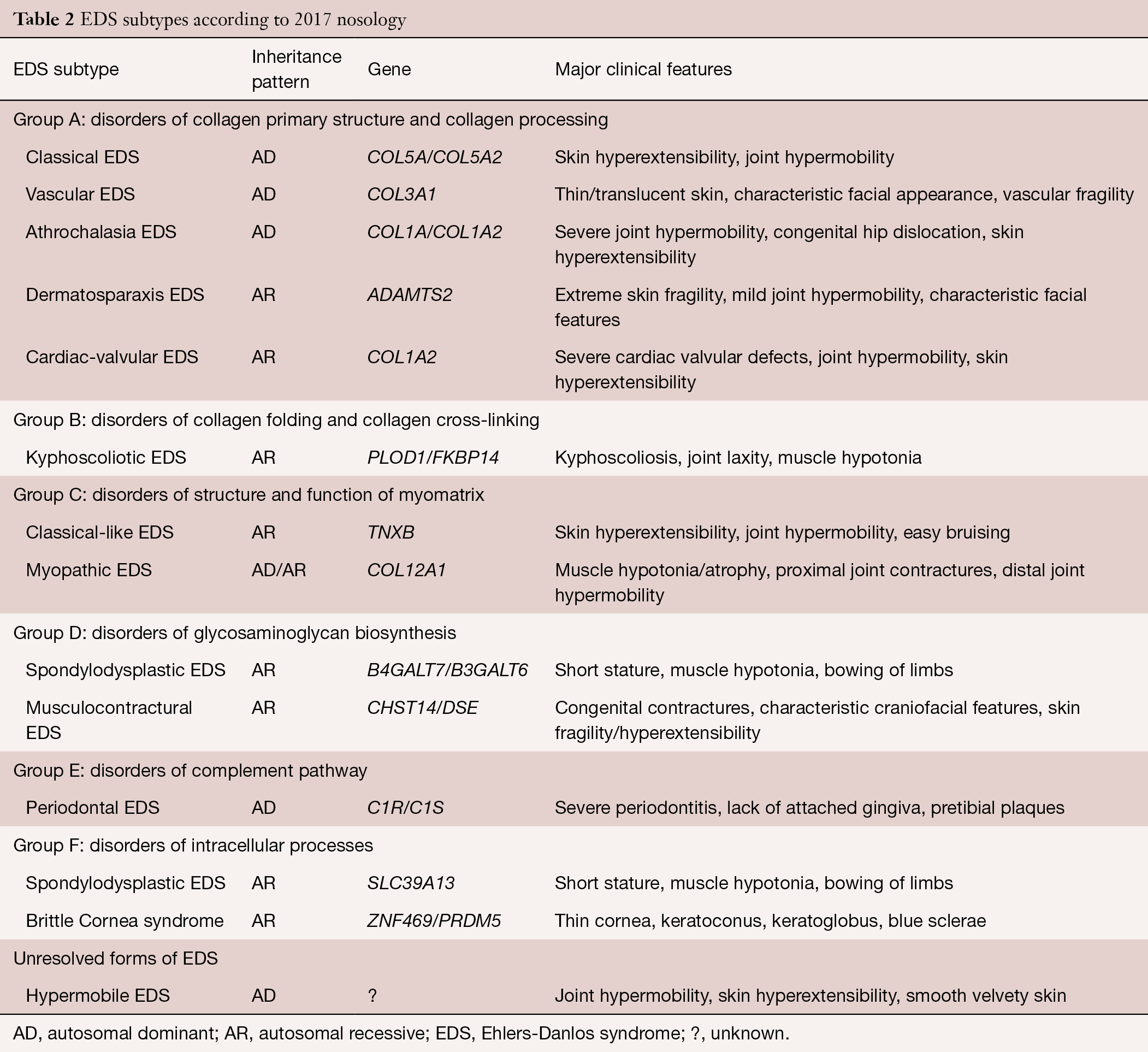
The syndrome was originally thought to have five cardinal features and recently a sixth was added on the basis of which a diagnostic criteria was developed. Joint hypermobility affecting both large elbows knees and small fingers toes joints. EhlersDanlos syndromes are a group of rare genetic connective-tissue disorders.
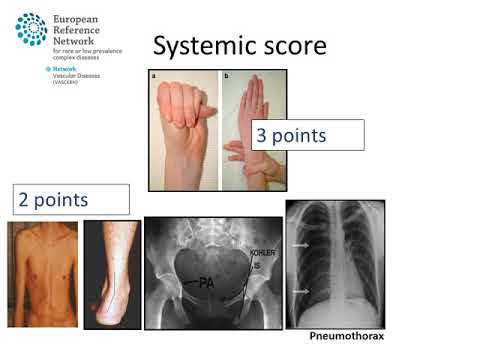
The likelihood of finding a pathological mutation in FBN1 in a patient with classic Marfan syndrome according to the Ghent criteria is 95. 4 primary features or 3 primary features and 2 secondary features must be present. Symptoms may include loose joints joint pain stretchy velvety skin and abnormal scar formation.
EDS occurs due to variations of more than 19. Complications may include aortic dissection joint dislocations scoliosis chronic pain or early osteoarthritis. Diagnostic criteria are meant solely to distinguish an EDS from other hereditary disorders of connective tissue.
The journals editor E. A confirmed diagnosis requires coordinated evaluation by a cardiologist ophthalmologist orthopaedic surgeon and geneticist all experienced with Marfan syndrome.
Genetic counseling and testing for Alzheimer disease.
The likelihood of finding a pathological mutation in FBN1 in a patient with classic Marfan syndrome according to the Ghent criteria is 95. Diagnostic criteria are meant solely to distinguish an EDS from other hereditary disorders of connective tissue. It was published in the Journal of Medical Genetics. Pediatric Neurology features up-to-the-minute publication of the latest advances in the diagnosis management and treatment of pediatric neurologic disorders. Joint hypermobility affecting both large elbows knees and small fingers toes joints. Dean JA Blanchette VS Carcoa MD et al. A confirmed diagnosis requires coordinated evaluation by a cardiologist ophthalmologist orthopaedic surgeon and geneticist all experienced with Marfan syndrome. As further understanding is gained some aspects of the classification may change. Due to the widespread role of connective tissue throughout the body individuals with Marfan syndrome may be at risk for many potentially severe or lethal co-moribidities as a result of the disease process.
Evaluation of the Adolescent or Adult with Some Features of Marfan Syndrome. Frequent joint dislocations and subluxations partial dislocation often affecting the shoulder kneecap andor temporomandibular joint joint that connects the lower jaw to the skull. Evaluation of the adolescent or adult with some features of Marfan syndrome. Dean JA Blanchette VS Carcoa MD et al. Diagnostic criteria are meant solely to distinguish an EDS from other hereditary disorders of connective tissue. The primary features are. Due to the widespread role of connective tissue throughout the body individuals with Marfan syndrome may be at risk for many potentially severe or lethal co-moribidities as a result of the disease process.

































Posting Komentar untuk "Marfan Syndrome Diagnostic Criteria"