unsweetened shredded coconut nutrition
 Unsweetened Shredded Coconut - Buy Online | Bob's Red Mill Natural Foods
Unsweetened Shredded Coconut - Buy Online | Bob's Red Mill Natural FoodsCoconut nutrition data and health benefits Shereen Lehman, MS, is a health reporter and fact checker. He has co-authored two books for the popular Dummies series (like Shereen Jegtvig). Mia However, MS, RDN is a diet nutritionist registered with a science master in human nutrition. She is also the host of Good Food Friday at ABC News 4. Very well / Alexandra Shytsman The nuciferous coconut (Coco nucifera) are the seed and fruit of the palm tree family. They are found in tropical regions where they are harvested by their white meat, oil and juices. In the United States, fresh whole coconut is considered an exotic food and is consumed mainly by health enthusiasts. However, with its increase in popularity, it is becoming easier to find whole coconuts or coconuts in local markets. The crushed coconut is commonly found in grocery stores. Coconut can be a delicious and nutritious addition to your diet when consumed in moderation. Despite being high in saturated fat, coconuts provide manganese and fiber. Coconut nutrition data The following nutritional information is provided by USDA for a piece (45g) of fresh 2" x 2" x 1/2" coconut meat. Coconut nutrition data Carbs A piece of fresh coconut meat and no sugar has only 6.8 carbohydrates, most of which is insoluble fiber, an undetectable form of dietary carbohydrate. provides bulk to feces, and can help prevent constipation and the development of hemorrhoids. There is a small amount of naturally-curring, but only 2.8 grams per serving. It is estimated that the glycemic load of a single portion of fresh coconut meat is approximately 6. Fats There are 15 grams of fat in a single portion of coconut meat. Most of the fat (13.4g) is saturated fat. There is also a small amount of monounsaturated fat (0.64g) and a lower amount of polyunsaturated fat (0.16g). Coconut is one of the highest vegetable sources of saturated fat. Saturated fat is the type derived mainly from the protein of the meat. It is associated with hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol), atherosclerosis (difference of the arteries), and heart disease. There has been a substantial debate in the health and research environments on the relative risks and benefits of different types of fat in coconut and coconut oil. Coconut provides medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs). Some consider that MCFAs are healthier than long-chain fatty acids (founded in meat and dairy sources). However, coconut fat provides 9 calories per gram, as well as all fats. So it's smart to consume it in moderation. Protein Coconut meat is not a rich protein source, but it provides about 1.5 grams per piece. Vitamins and Minerals A single portion of coconut meat provides 34% of the daily value for manganese, a mineral that helps your body maintain a healthy brain, nervous system, and immune function. It will also benefit from other coconut minerals including copper (10%), selenium (6%), iron (6%) and small amounts of phosphorus, potassium, magnesium and zinc. Coconut is not a significant source of vitamins, but there are small amounts of folate, vitamin C and thiamine. Health benefits Crocodiles have gained popularity for their anti- disease properties, but many of the claims are not supported by research or simply inflated by food manufacturers. Coconut meat has not been studied as widely as coconut oil, which is derived from coconut meat. Note that while you can get certain benefits from coconut oil when you consume coconut meat. But meat produces much less oil than a comparable portion of oil. Cholesterol improvement Some coconut oil advocates believe it is much better for their health than to consume other forms of saturated fat. Coconut oil is often promoted by its beneficial effects on cholesterol levels. The fat in the coconut comes mainly from lauric acid, a medium-chain fatty acid. This type of fat breaks down faster and does not accumulate in the bloodstream as much as long-chain fatty acids found in meat and dairy products. On the other hand, medium-chain saturated fatty acids are absorbed directly from the intestine and sent directly to the liver to be quickly used for energy production. They do not participate in biosynthesis and the transport of cholesterol. For this reason, some believe that coconut can lower "bad" LDL cholesterol. But studies have shown that coconut oil can raise your LDL cholesterol. A published study found that coconut oil raised LDL cholesterol less than butter, but significantly more than unsaturated vegetable oils. However, there are some potentially positive tests in relation to coconut oil and HDL levels. HDL cholesterol is considered a "good" cholesterol. Some studies have found that consuming coconut oil can increase HDL levels. Researchers suggest that HDL increase may be due to high levels of lauric acid and myristic acid. Decrease in infections Research published in the July 2018 issue of the Journal of Food Science suggests that coconut fatty acids contain powerful antioxidants that help increase immune function and reduce systemic inflammation in the body. The authors of the study point out that these antioxidants can help protect the body from infections. Weight loss Many coconut fans and coconut oil claim that it can help reduce collapse. A review of 2018 studies supported certain claims related to weight loss, suggesting that the middle-chain triglycerides in coconut and coconut oil could improve fat burning, increased energy costs and even suppress appetite, but only if included as part of a low-fat diet. Another analysis of studies published in 2015 compared the consumption of middle-chain triglycerides (MTC) as those found in long-chain triglycerides (LTC) coconut oil for weight loss purposes. The authors of the study concluded that replacing TCLs with TCMs in the diet could potentially induce modest reductions in body weight and composition. The authors of the study noted, however, that independent research groups require more research using large and well-designed studies to confirm these findings and determine the dosage necessary for the management of a healthy body weight and composition. Heart disease There are numerous controversial claims that coconut can prevent heart disease. Many of these statements are based on the fact that people from tropical areas where coconuts are consumed widely traditionally had a lower risk of heart disease. According to the epidemiological research published in 1981, Tokelauans, for whom coconut accounts for 60 per cent of the daily diet, had no evidence of heart disease or hypercholesterolemia despite the high intake of lauric and myristic acid. But researchers also point out that these people also ate diets rich in fish and vegetable foods. Many scientists now believe that the cardioprotective properties of coconut consumption have been exaggerated. In fact, a major review of studies found little evidence supporting the fact that consuming coconut or coconut oil (instead of unsaturated oil) reduced the risk of heart disease. More recent assertions that coconut meat, coconut milk or coconut oil can increase mental function in people with Alzheimer's disease remains largely unsupported. Reduced cell damage Coconut and Coconut Oil is known to provide antioxidants These antioxidants can help reduce oxidative stress and reduce the risk of metabolic and age-related diseases by eliminating free radicals that cause cell damage. Allergies Coconut allergy is rare but can occur, especially in people with a known allergy to nuts or other nuts. If an allergy occurs, it is most likely in the form of contact dermatitis, an allergic reaction caused when coconut or coconut oil comes into contact with the skin. Coconut-derived compounds, such as diethanolamine, cocalide sulfate and coca-based DEA, are sometimes found in cosmetics. Less commonly, people may experience a food allergy after eating coconut. Symptoms may include nausea, stomach pain, swelling of the lips, spongy nose, diarrhea, vomiting, and a sensation of irritation or burning of the mouth. Anaphylaxia, a life-threatening reaction of the whole body, is exceptionally rare when eating coconut, according to a 2017 study by the University Hospital of Texas. Even so, coconuts are classified as nuts by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and must be revealed as a possible allergen in food labels. Adverse effects There are no known drug interactions for coconut or coconut oil. Variants People often wonder if the coconut is a fruit, a vegetable or a walnut. In fact, coconut is a seed bud. A breakage is a fruit that has a hard cover on the seed, like a peach or cherry. The nuts, almonds and nuts are also buds, but we usually refer to them nuts. It can take a lot of work to extract coconut from all the fruit, so many people buy coconut or freshly crumbled or dried and crushed. Liquids inside are available as coconut milk or . A portion of a dried coconut indula has a little more calories than a portion of fresh coconut. However, many crushed coconut brands add some sugar during processing. A half cup (100 grams) of grated and sweetened coconut provides 500 calories, almost 48 grams of carbohydrates, 43 grams of sugar, 35 grams of fat and 2.8 grams of protein. The nutritional value of other foods and coconut beverages can vary substantially. When it's better Crocodiles grow throughout the year in tropical and subtropical regions. However, if a coconut tree is planted, it may take 12 to 13 years for the tree to bear fruit. You can see brown and green coconuts in the store. They are the same variety, but they differ in age. Green coconuts are younger and have less meat. Brown coconuts are totally ripe and have less juice. To choose the best coconut in the store, find one that feels heavy for its size. Shake the coconut and listen to liquid inside. Avoid coconuts with cracks. Storage and Food Safety An entire coconut can be stored at room temperature for up to four months. Once opened, refrigerate the coconut meat up to a week. You can also freeze it up to three months. Coconut milk should also be refrigerated and consumed within three days. If you buy a crushed coconut package, keep it in a hermetic container. It should be kept fresh for four to six months stored at room temperature. The fresh crushed coconut should be treated as a fresh whole coconut that has been opened. He has a much shorter shelf life. How to prepare An entire coconut shell is extremely hard. While some people will tell you to break it against a concrete floor to break the shell, you are likely to lose many of the juices inside. Instead, try to bomb a coconut with five simple tools: a hammer or deck, a long metal mower, a butter knife, a vegetable peeler and some kitchen towels. To break a whole coconut: Use toasted coconuts like a topping for desserts and side dishes, or add it to a mix of trails or your favorite granola recipe. You can also incorporate it into baked products. It's easy to provide coconut. Start preheating the oven to 325c F. Spread thin coconut flakes in a baking sheet and place them in the oven for about five or 10 minutes until golden brown. Watch 'em because they're brining quickly. It helps to stir them up once or twice to brown evenly. Recipes Healthy Coco Recipes to TryGet nutritional advice and advice to facilitate healthy eating. Thank you, for signing. There was a mistake. Please try again.. USDA FoodData Central. 4/1/2019 Mcrorie JW, Mckeown NM. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2017;117(2):251-264. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2016.09.021Siri-tarino PW, Sun Q, Hu FB, Krauss RM. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91(3):502-9. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2008.26285 Boateng L, Ansong R, Owusu WB, Steiner-Asiedu M. . Ghana Med J. 2016;50(3):189–196. Eyres L, Eyres MF, Chisholm A, Brown RC. . Nutr Rev. 2016;74(4):267–280. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuw002Chinwong S, Chinwong D, Mangklabruks A. . Complement of Evid Alternat Med. 2017;2017:7251562. doi:10.1155/2017/7251562Patil, U, Benjakul, S. J Food Sci. 2018;83. doi:10.1111/1750-3841.14223 Wang, Y, Liu, A, Han, Y, et al. PLoS ONE.2018;13(2):e0191182. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0191182Mumme K, Stonehouse W. . J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015;115(2):249-63. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2014.10.022Prior, I, Davidson, F, Salmond, C, et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981;34(8):1552-61. doi:10.1093/ajcn/34.8.1552Sankararaman S, Sferra TJ. Curr Nutr Rep. 2018;7(3):107-115.doi: 10.1007/s13668-018-0230-5Li Y, Zheng Y, Zhang Y, Xu J, Gao G. . Molecules. 2018;23(3):707. doi:10.3390/molecules2303070707. National Center for Complimentary and Integrative Health. Updated May 04, 2016. American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Updated 4/25/19Anagnostou, K. Children (Basel). 2017;4(10):85. doi:10.3390/children4100085.Sprouse AA, van Breemen RB. . Drug metastasis. 2016;44(2):162-171. doi:10.1124/dmd.115.066902. USDA FoodData Central. Updated 4/1/2019. United States Department of Agriculture. 4/1/2019 Department of Agriculture of the United StatesData Central. 4/1/2019. United States Department of Agriculture. Updated 4/1/2019 Thank you, for signing. There was a mistake. Please try again.

Edward & Sons, Let's Do Organic, 100% Organic Unsweetened Shredded Coconut, 8 oz (227 g) - iHerb

Organic Shredded Coconut - Unsweetened - Sweet & Sprouted Canada

ONE LIFE ORGANIC Desiccated Coconut - Unsweetened Shredded Coconut Powder - 300g - Vegan, Gluten free, Ready-to-cook Grated Coconut Flakes - Certified Organic Products Online Organic Grocery Store Near You Onelife Organic

Unsweetened Coconut Flakes Benefits And Recipes – Melanie Cooks

Coconut Shredded Unsweetened Nutrition Facts - NutritionWalls
Unsweetened Shredded Coconut (7oz) - Explorado Market

Now Foods Real Food, Organic Coconut, Unsweetened, Shredded, 284g: Amazon.sg: Grocery & Gourmet Food

Edward & Sons, Let's Do Organic, 100% Organic Unsweetened Shredded Coconut, Reduced Fat, 8.8 oz (250 g) - iHerb

Let's Do Organic® Unsweetened Shredded Coconut – Edward & Sons Trading Co.

Substitute Unsweetened for Sweetened Coconut | Mother Would Know
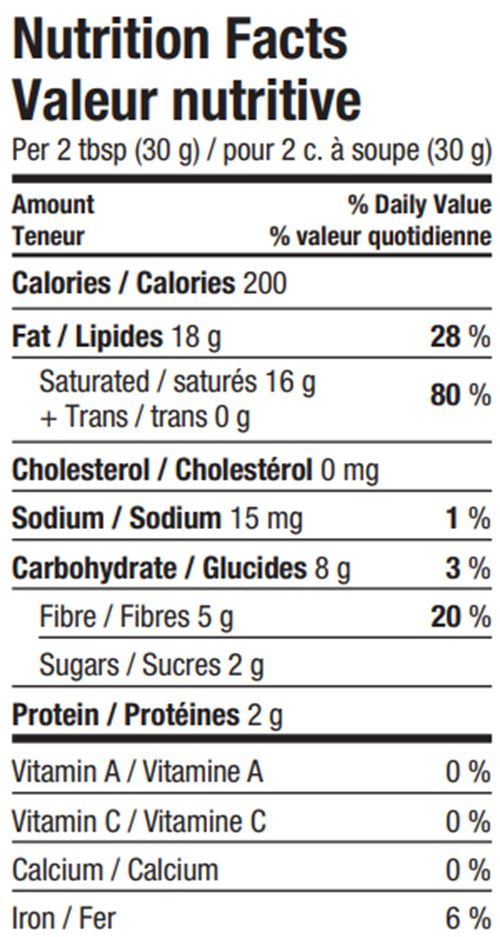
Great Value Unsweetened Shredded Coconut | Walmart Canada

Unsweetened Shredded Coconut 2 lb, Shredded Coconut Flakes

O Organics Organic Coconut Shredded Unsweetened - 12 Oz - Jewel-Osco

Now Foods, Real Food, Organic Coconut, Unsweetened, Shredded, 10 oz (284 g) - iHerb

Unsweetened Coconut Flakes Nutrition Facts - Eat This Much

One Life Organic Desiccated Coconut - Unsweetened Shredded Coconut Powder - 300g - 2 Pack - Vegan, Gluten Free, Ready-to-Cook Grated Coconut Flakes: Amazon.in: Grocery & Gourmet Foods
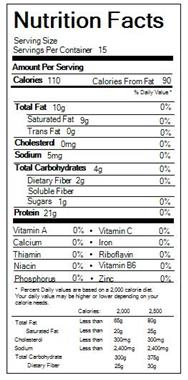
Let's Do...Organic 100% Organic Shredded Coconut Unsweetened | Hy-Vee Aisles Online Grocery Shopping

Bob's Red Mill Unsweetened Shredded Coconut, 12 oz - Metro Market

King Soopers - Bob's Red Mill Unsweetened Shredded Coconut, 12 Oz

Bob's Red Mill Shredded Unsweetened Coconut ‑ Shop Coconut Flakes at H‑E‑B

Organic Raw Unsweetened Coconut - Shredded| Northfork Naturals

Is Unsweetened Shredded Coconut Paleo - Paleo Plan
The Whole Kitchen Singapore - Organic Desiccated Coconut

Let's Do Organic 100% Organic Shredded Coconut Unsweetened - 8oz : Target

Coconut Shredded (Unsweetened)
Health Paradise Organic Unsweetened Shredded Coconut 200gm ( Gluten Free ) | Shopee Singapore

Unsweetened Coconut Flakes Benefits And Recipes – Melanie Cooks

QFC - Bob's Red Mill Unsweetened Shredded Coconut, 12 oz

Organic Unsweetened Shredded Coconut, 8 oz at Whole Foods Market

Mariano's - Bob's Red Mill Shredded Unsweetened Coconut, 24 oz

Bob's Red Mill Dried Coconut Shredded

Ralphs - Bob's Red Mill Unsweetened Unsulfured Coconut Flakes, 10 oz

Coconut Flakes | Bob's Red Mill

Unsweetened Shredded Coconut - anuts.com

Great Value Unsweetened Shredded Coconut | Walmart Canada

Harris Teeter Unsweetened, Shredded Coconut - 7 oz, Nutrition Information | Innit

Unsweetened Shredded Coconut Nutrition Facts - Eat This Much

Health Paradise Organic Unsweetened Shredded Coconut 200gm Gluten Free, GF

One Life Organic Desiccated Coconut - Unsweetened Shredded Coconut Powder - 300g

H‑E‑B Organics Unsweetened Coconut Flakes ‑ Shop Coconut Flakes at H‑E‑B
Posting Komentar untuk "unsweetened shredded coconut nutrition"