 Scary Truth: Does Medicare Cover Hip Replacement Surgery?
Scary Truth: Does Medicare Cover Hip Replacement Surgery?Knee replacement surgery Make Dr. Alan Cheung your choice Joint replacementTotal Knee Replacement (TKR) is an effective solution to consider knee pain and deformity due to osteoarthritis, rheumatoid or post-traumatic arthritis. TKR is one of the most common orthopaedic surgeries performed worldwide and can lead to a dramatic improvement in quality of life. During a TKR, the worn surface of the knee is removed and replaced with metal and plastic components through an incision on the front of the knee. Younger patients or those with pain located on the side of the knee joint can be suitable for a Unicompartmental (UKR) knee replacement. This surgery can be performed using a robot (see Robotic Surgery section on the website). Causes of Knee PainOsteoarthritis – wear related to degenerative age, leading to loss of cartilage, knee stiffness and deformity. This usually occurs in patients over 50 years of age, but it may occur in younger patients. Smaller patients may be more suitable for unilateral knee replacement (UKR). Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid arthritis – an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the lining of the knee joint (synovitis) that leads to joint destruction. This may affect many joints and body organs, and may occur in younger patients. It is part of a spectrum of conditions called 'inflammatory atropathies' and is treated with the help of a rheumatologist (medical mixed specialist). Rheumatoid arthritis Post-Traumatic Arthritis – This can follow a lesion in the cartilage or bone fracture. Over time you can lose more cartilage and a degenerative change may occur. Post-Traumatic Arthritis If your knee pain is severe and has difficulty walking, climbing stairs and having pain at night, you can be a suitable candidate for TKR or UKR. It can also have a stiff and deformed knee. If you have tried to take painkillers, physiotherapy exercises and even knee joint injections (such as steroid or hyaluronic acid injections) unsuccessful, joint replacement may be the next step for you. In the consultation, a careful history and examination is taken to evaluate the severity of your joint disease, and to exclude the related pain of the spine and spine. You will have x-ray weight of the knees to accurately evaluate the degree of joint damage. Some patients also receive a CT scan if they undergo robotic surgery or even other surgery services. A careful discussion will take place with you about the risks and benefits of the procedure and what to expect in the long term. You should feel free to ask questions, and express any fear and concern you have regarding orthopaedic surgery. Please bring a close friend or family too, as my goal is to ensure that you and your family are well informed and prepared, and have realistic expectations regarding surgery. Patients with active infection, lack of sensation in the joint of the knee, poor muscle function in their thigh muscles (quadriceps), as well as severe medical conditions such as blood vessel disease in the leg (blue block and peripheral vascular disease) may not be suitable for TKR or UKR or may need to undergo medical treatment first. Often I am asked this question by patients' relatives. The answer is no – it depends on your general health and what you can get from surgery, instead of your absolute age. Older people tend to suffer more than a worn knee joint and therefore are more likely to need a joint replacement. I replaced the knee joints of patients over 90 years old, who went to enjoy their remaining years without knee pain. With regard to younger patients, I have also treated patients in their 40 years who have severely used parts of their knees and have benefited from a partial or total replacement of the knee. Knee replacement for the right reasons can be suitable for all adult age groups. The joint of the knee can be divided into three compartments: the inside of the knee (middle part), the outside of the knee (side side part) and the space between the knee and the thigh bone (pathethefemoral joint). Patients suitable for TKR may have loss of cartilage in the three compartments, have severe deformity, ligamentous injury or joint inflammatory disease. Appropriate patients for UKR may have joint disease located in a single compartment. Both procedures can be performed with an excellent degree of precision using a robotic system such as Makoplasty, Navio or Robodoc. Some of the UKR's potential advantages over TKR include a smaller incision, less tissue damage and postoperative pain, less blood loss, faster recovery and return to work/sport, higher postoperative movement range. For those with two worn knees, replacing both sides at once (bilateral joint replacement) is an option. Replace both knees means a longer operation and an anaesthetic time, as well as a higher risk of complications. Recovery is a little longer than having a replaced knee. However, it means you don't have to worry about having to take more time off in the future to have the second knee replaced and also avoid the cost of a second hospitalization. Once you have decided to have a knee replacement, you will be checked for any medical condition that may need treatment, and will undergo a series of tests such as chest X-ray, electrocardiogram, and blood test. You should stop smoking immediately. You are advised to stop slimming blood medications and TCM herbs (which may also cause bleeding) two weeks before your surgery. The anesthetist can offer you a general anesthesia (where you are asleep during the procedure) or a spinal anesthesia (injection to the column that sleeps the legs). He won't feel anything during the operation. On the day of surgery, for safety reasons it is important not to eat or drink anything 8 hours before the procedure. Whenever possible, I perform my joint replacements through a small incision (about 10 cm or less). Complex and review cases may not be suitable for minimally invasive surgery. Body tissues are handled very smoothly during surgery. During the procedure I remove the worn joint surfaces from the thigh bone (femur) and the tibia bone. I worry about balancing soft tissues so that the knee is stable along the range of motion. It replaces the joint surface with metallic implants (usually cobalt chromium alloy) that are cemented on the bone. Finally, a plastic coating (highly linked polyethylene) is placed between the two metal surfaces to allow a smooth slide movement and reduce friction. During surgery I use a technique called local infiltration anesthesia that involves injecting a local anesthesia into cut tissues. This combined with an improvement of the possibilities of rapid recovery. I appreciate that pain is the main fear of patients, and I do my best to ensure that pain is minimized after surgery. As a result, most patients can stay and walk hours after surgery. He usually takes less than an hour. After the operation you will be transferred to the recovery area where you will be monitored for several hours until it is suitable for reloading to the general pavilion. Whenever possible, I want my patients to stand and walk immediately after surgery. I work closely with my physiotherapy colleagues to follow an improved recovery protocol so that patients begin to exercise day 1 of surgery. The ultimate goal is to download the room in or before Day 3 of the surgery. All surgical procedures have a risk element and possible complications. Fortunately the risks are generally low. Usually after surgery there may be temporary pain, swelling, bruising and stiffness. You'll take medicine to relieve pain. The infection is the main concern (about risk 1%) after joint replacement, and is taking great care during surgery to reduce this risk, including antibiotic treatment during after surgery through drip. A blood clot in the legs (deep vein thrombosis) or lungs (pulmonary embolism) is less common, and precautions such as foot mechanical pumps and/or blood thinning medications are used to reduce your risk. You will have an in-depth discussion with your knee surgeon about the potential risks of surgery. The wound may take 2 weeks to heal and it is important to keep it clean and dry during this time. Patients may need to use crutches or walk aids for several weeks after surgery. It is very important to do knee exercises and assist physiotherapy to get the best out of surgery. Most patients can drive six weeks after knee replacement. It is recommended not to fly long long lengths for at least six weeks after surgery to reduce the risk of blood clot in the legs (deep vein thrombosis) or lungs (pulmonary embolism). Patients undergoing UK RK may sometimes return to work six weeks or before depending on their occupation. Patients undergoing full replacement knee often need more time to recover – on average between six to twelve weeks in my experience, although there are exceptions. In the days and weeks following the surgery, you will be followed closely, to monitor your progress, general well-being and to monitor any complication that may occur. My goal is to relieve your pain and restore function to your limbs through joint replacement. Although it may take some time and effort to recover, most patients can achieve an excellent result. Dr. Alan Cheung is an orthopaedic surgeon specializing in the treatment of sports injuries such as broken ligaments and tendons, fractures and sprains, cartilage lesions and even bone cancer. He is an expert in minimally invasive joint reconstruction and the use of advanced robotic surgery (Makoplasty, Navio and Robodoc) for better surgical results and reduce downtime. Do you need quick advice? Please fill in the form below and we will return to you within the day.#05-24 Mount Elizabeth Novena Specialist Centre38 Irrawaddy Road, Singapore 329563 Tel : Fax : Whatsapp : Operating hours: Monday to Friday - 9.00 AM - 5.00 PM Saturday - 9.00 AM - 1.00 PM Closed on Sundays and holidays
Does Medicare cover hip replacement? Medicare usually covers hip replacement surgery, providing a doctor confirms that the procedure is medically necessary. Hip replacement surgery may help someone walk easier and lead a healthier life. The Health Research and Quality Agency reports the termination of more than hip replacements each year in the United States. In this article, we give an overview of what plans cover hip replacement and what the surgery involves. Below, we provide details of each separate plan coverage, eligibility and costs. We can use some terms in this piece that can be useful to understand when selecting the best insurance plan: We can use some terms in this piece that can be useful to understand when selecting the best insurance plan: If someone has hip pain because of , a , or other condition, it can be difficult or painful to do daily activities. The original Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans provide help with the costs of hip replacement surgery. Part of Medicare D provides coverage for prescription drugs that someone needs for home recovery. An individual will also have expenses outside the pocket, such as deductibles and copayments. If someone has a Medicare supplement (Medigap) plan from a private insurance company, the plan could help the costs. For more resources to help you guide through the complex world of health insurance, visit our . Doctors use the term full hip arthroplasty for hip replacement surgery. Surgery involves an artificial joint. It is an option for people who have used other treatments and pain relief without positive effects. Surgeons can use a traditional or surgical technique. The main difference between these methods is the length of incision. The conventional technique requires a cut along the hip joint, while the minimally invasive technique can use one or two smaller cuts. For any type of surgery, an individual needs general or spinal anesthesia. During surgery, the surgeon cuts the thigh bone and removes any damaged tissue and the damaged hip joint. Then attach an artificial joint to the thigh bone with surgical cement or screws. After the surgeon replaces the joint, closes the muscles and skin, and can insert a drainage tube. People usually spend between days recovering in the hospital after their hip replacement surgery. Full recovery may take months. Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) covers several costs related to hip replacement surgery. Medicare Advantage plans have to match this level of coverage. A Medigap plan can also help with the costs. More details are shown below. Part of Medicare Ensuring a stay in a Medicare-approved hospital, Medicare Part A, which is hospital insurance, provides coverage for certain expenses: Sometimes people need more time to recover from their surgery and move to a specialized nursing center (SNF). Part of Medicare A covers the first of a stay in a SNF, including . Part B of MedicareBefore someone has hip replacement surgery, they will need several minor external patient procedures to prepare for the procedure. First, a general physical exam will check if a person is healthy for surgery. At this point, you will need a full hip exam, and may need blood, X-ray or . Medicare Part B contributes to these outpatient costs. After surgery, Part of Medicare B can cover physical therapy as an outpatient, as well as cover the costs of durable medical equipment (DME) as a cane or walker. In some cases, a person may have hip replacement surgery in an outpatient surgical center, which means they will go home the same day as surgery. Part of Medicare B provides coverage for these costs. Medicare Part DPrivate insurance companies offer Medicare Part D plans that cover the prescription drugs that someone needs while at home. Part of Medicare One only covers drugs as a patient. Typically part D covers the prescription drugs needed during recovery of a person from hip replacement surgery. These medicines may include: MedigapPrivate companies sell Medigap policies. Plans are designed to help fill the "gaps" in the original Medicare coverage. If a person has a Medigap policy, he can get help with some costs. A person can use to compare the details of the plan. They may also want to check the cost coverage through the employer or the spouse. Both Part A and Part B of the original Medicare or Medicare Advantage plans generally cover hip replacement surgery if a doctor confirms that surgery is medically necessary. The price of hip replacement surgery in the USA varies between , according to the American Hip Association and Knee Surgeons. An individual should contact your doctor to find out more about the cost of your hip replacement surgery. In general, the amount that a person with Medicare coverage has to pay is affected by knowing deductibles and premiums. The annual deductible for Medicare Part A is $, and $ for Part B. Most people don't pay a premium for part A. For part B, the standard monthly premium is $.Medication A Part usually pays 100% of the remaining costs after payment of deductibles and premiums. Part of Medicare B pays 80% by leaving a person to pay the remaining 20%, plus deductibles and premiums. A person can if they have found their deductibles. People with arthritis or other damage to the hip joint may benefit from hip replacement surgery. Medicare usually covers hip replacement surgery if the procedure has been medically deemed necessary. The amount Medicare provides depends on several factors, including a person's Medicare plans, hospital and outpatient fees, and the state of surgery. People should confirm potential costs with their doctor and hospital before surgery. The information on this website may help you make personal insurance decisions, but it is not intended to provide advice regarding the purchase or use of any insurance or insurance products. Healthline Media does not transact the insurance business in any way and is not licensed as an insurance company or producer in any jurisdiction of the US. Healthline Media does not recommend or support third parties that may perform insurance transactions. Last medical review on July 22, 2020 Latest newsRelated coverage
Medicare and hip replacement: Coverage, eligibility, and costs
How much does a hip replacement cost, $95,459 or $77,967? Or, why does the insurance company pay more than the bill? - Clear Health Costs
How much does a hip replacement cost, $95,459 or $77,967? Or, why does the insurance company pay more than the bill? - Clear Health Costs
Medicare proposes outpatient hip replacements to cut costs - Axios
New Medicare model may improve care, cost for knee, hip surgeries - UPI.com
Hospitals leery of CMS proposal to pay for joint replacements in ASCs
What You Need to Know About Hip Replacement Surgery And Recovery?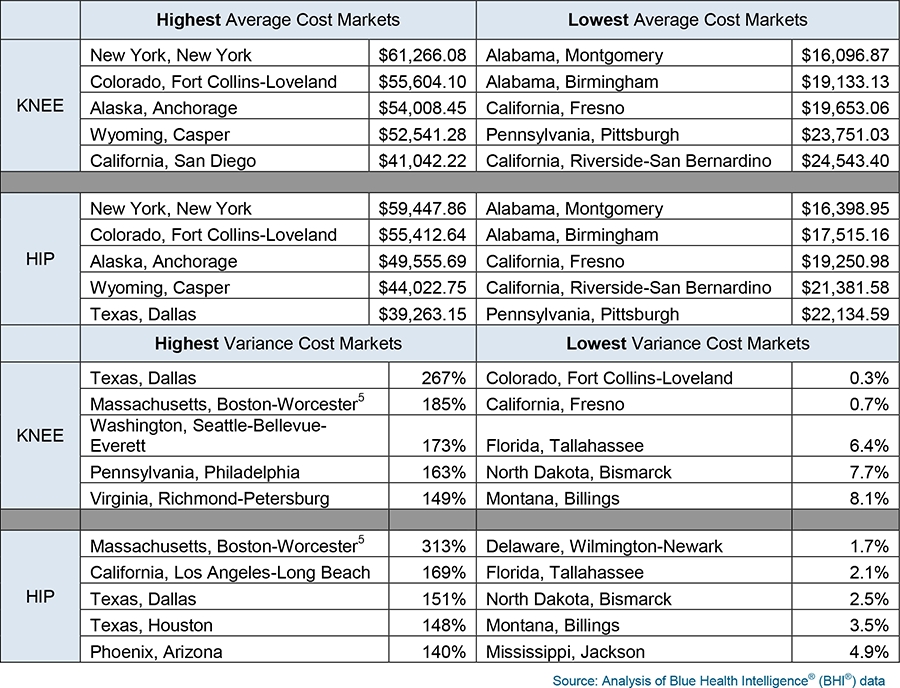
A study of cost variations for knee and hip replacement surgeries in the U.S. | Blue Cross Blue Shield
What You Need to Know About Hip Replacement Surgery And Recovery?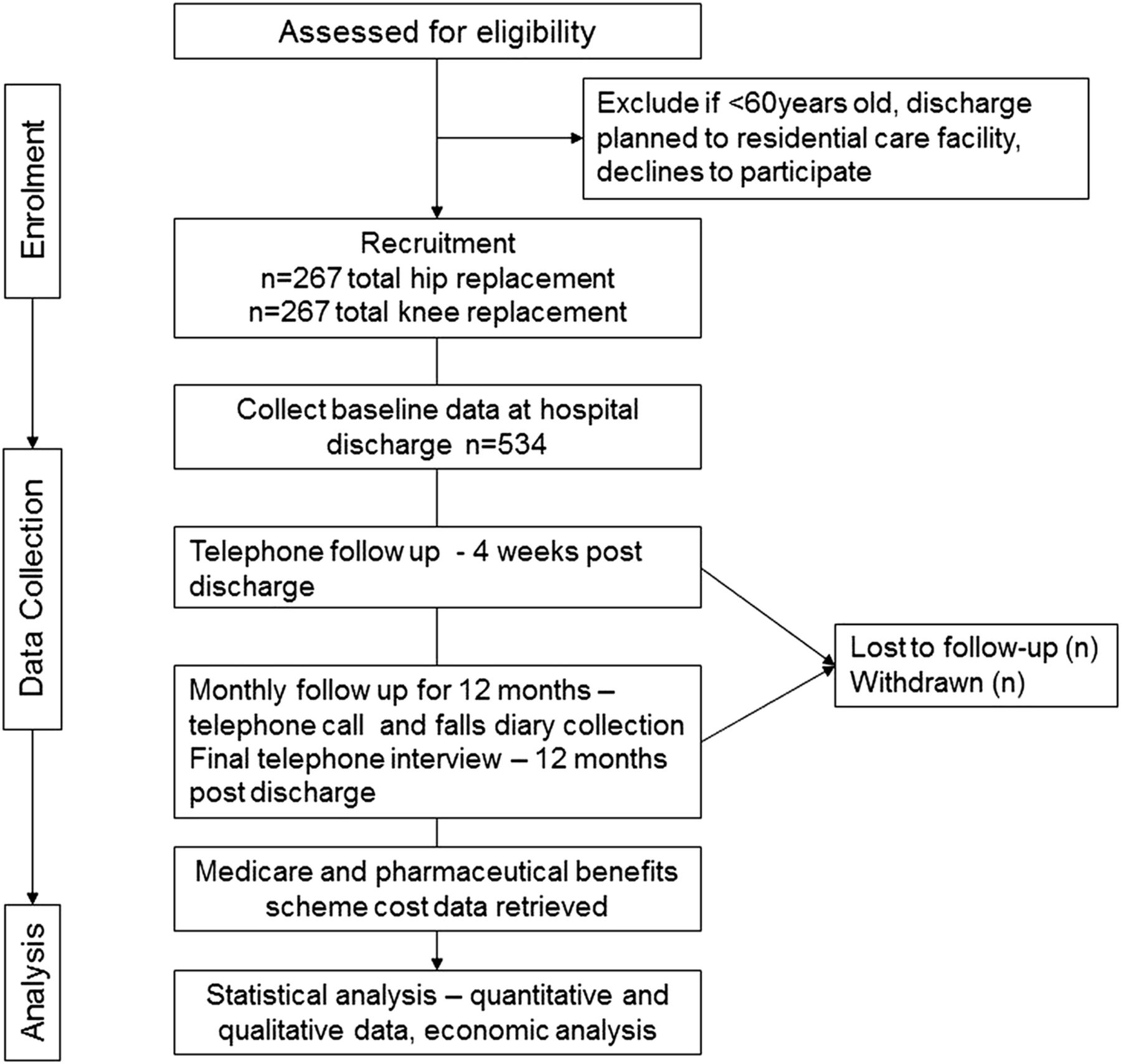
Incidence, risk factors and the healthcare cost of falls postdischarge after elective total hip and total knee replacement surgery: protocol for a prospective observational cohort study | BMJ Open
Price of a common surgery varies from $39,000 to $237,000 in L.A. - Los Angeles Times
Outcomes of Ceramic Bearings After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Medicare Population - The Journal of Arthroplasty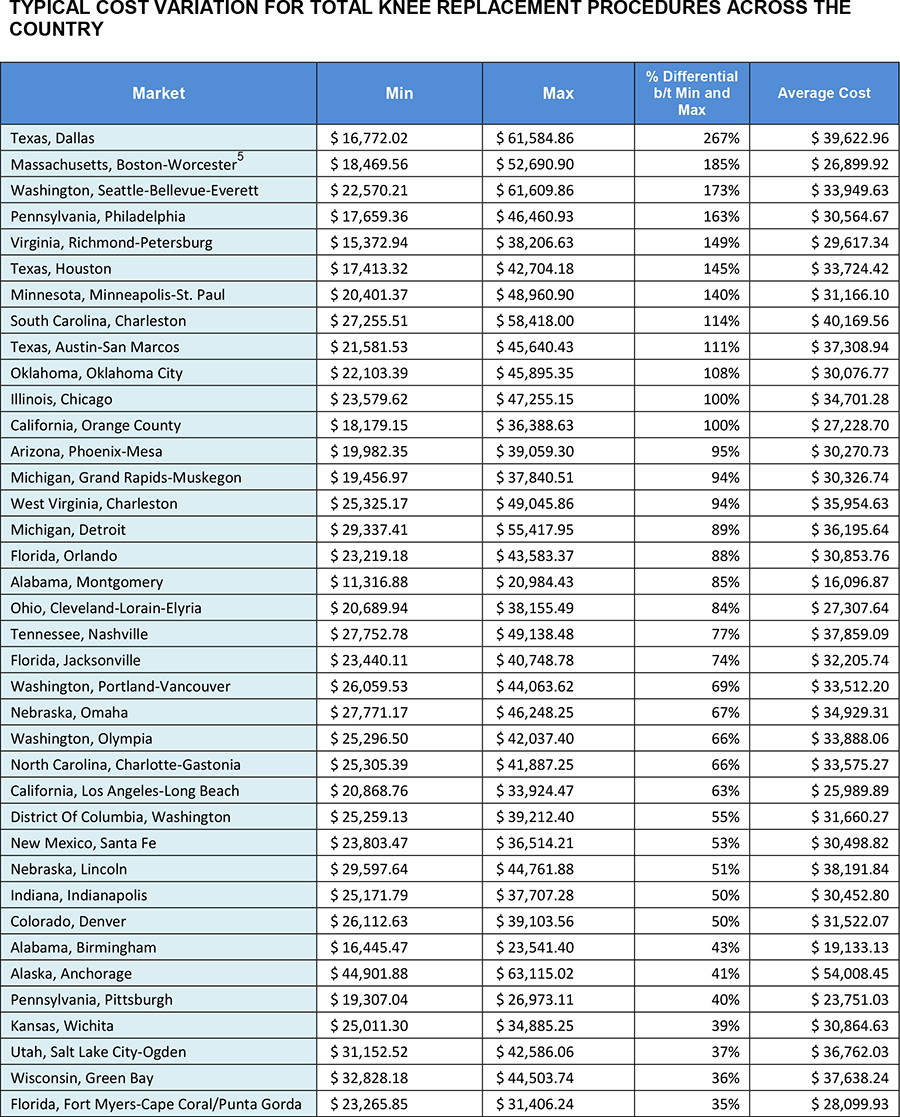
A study of cost variations for knee and hip replacement surgeries in the U.S. | Blue Cross Blue Shield
Joint venture: What a new hip or knee really costs - MarketWatch
Adoption of New Medical Technologies: The Case of Customized Individually Made Knee Implants - ScienceDirect![PDF) The Total]()
PDF) The Total "Economic Cost" of Primary Total Joint Replacement Surgery in the United States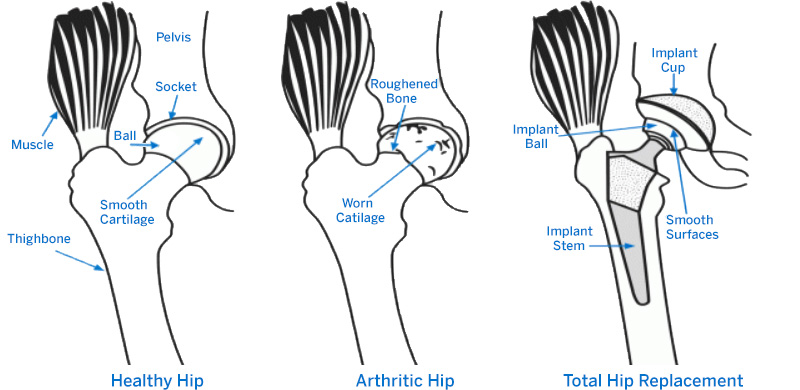
Hip Replacement Surgery: Procedure, Types and Risks | HSS
Joint replacement surgery costs vary greatly between hospitals
How Top Hospitals Control Joint Replacement Costs
Back Pain? Could Be Your Hips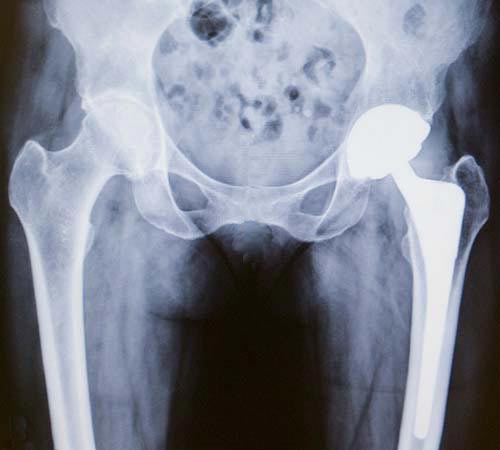
Hip Replacement Surgery: Procedure, Types and Risks | HSS
Medtronic Launches Low-Cost Hip and Knee Program Forecasts Surgical Robot Revenue By FY 2019
Joint Replacement Market | Growth, Trends, and Forecasts (2020-2025)
Total Hip Replacement: Anterior Approach | Johns Hopkins Medicine
Customized Knee Implants Drive Significant Cost Savings in a Medicare Population – Abstract Presented at Annual Knee Society Meeting – OrthoFeed/considering-hip-replacement-surgery-2549565-v11-3d3b7eafd288402d87af34c275996f26.png)
Hip Replacement Surgery: Things to Consider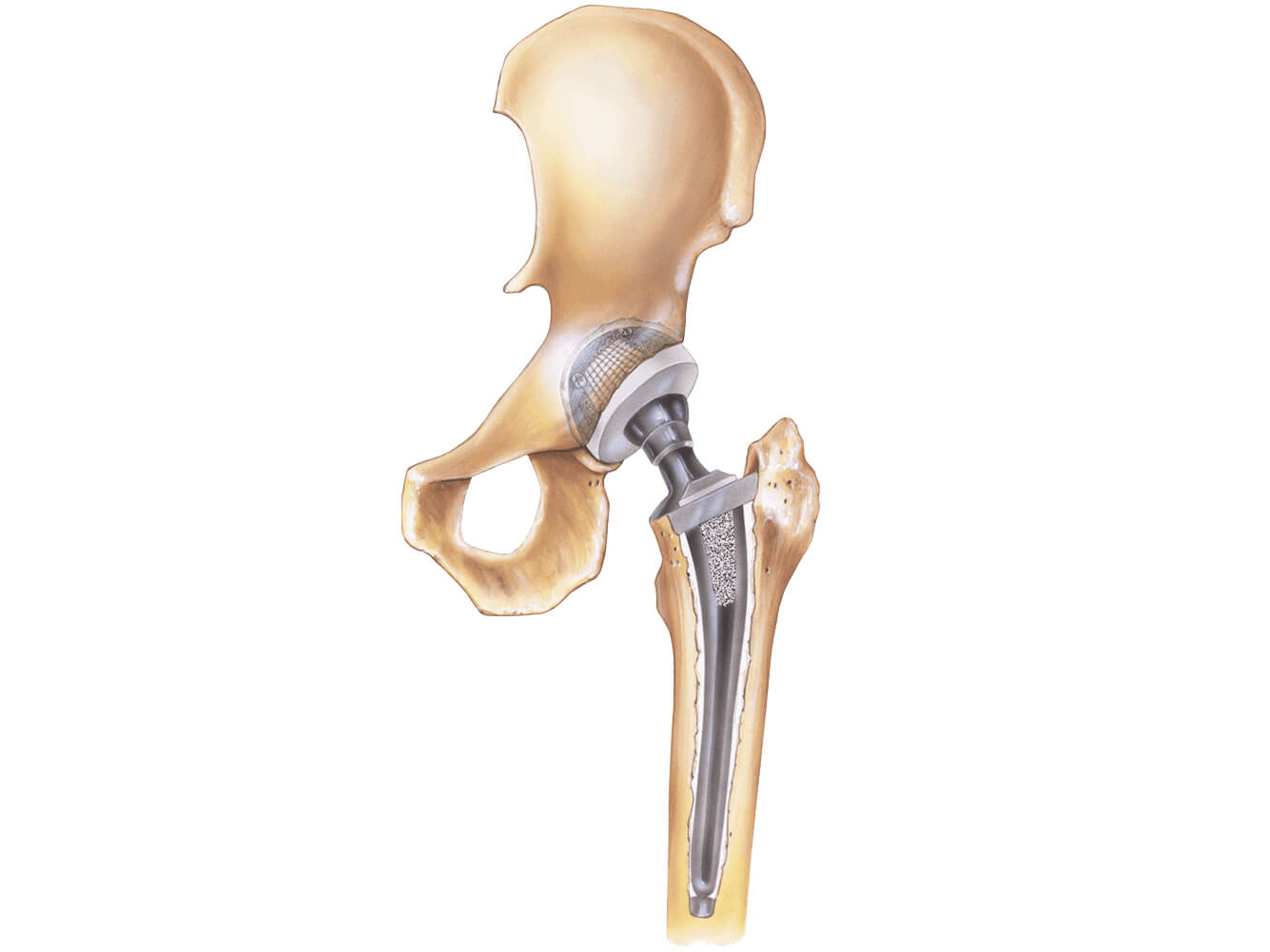
Hip Replacement Complications - Risk of Infection & Dislocation
Total Hip Replacement: Anterior Approach | Johns Hopkins Medicine
Hip & Knee Replacements: New Medicare Rules
How Much Does Minimally Invasive And Robotic Hip Replacement Surgery Cost? - Hip Replacement Info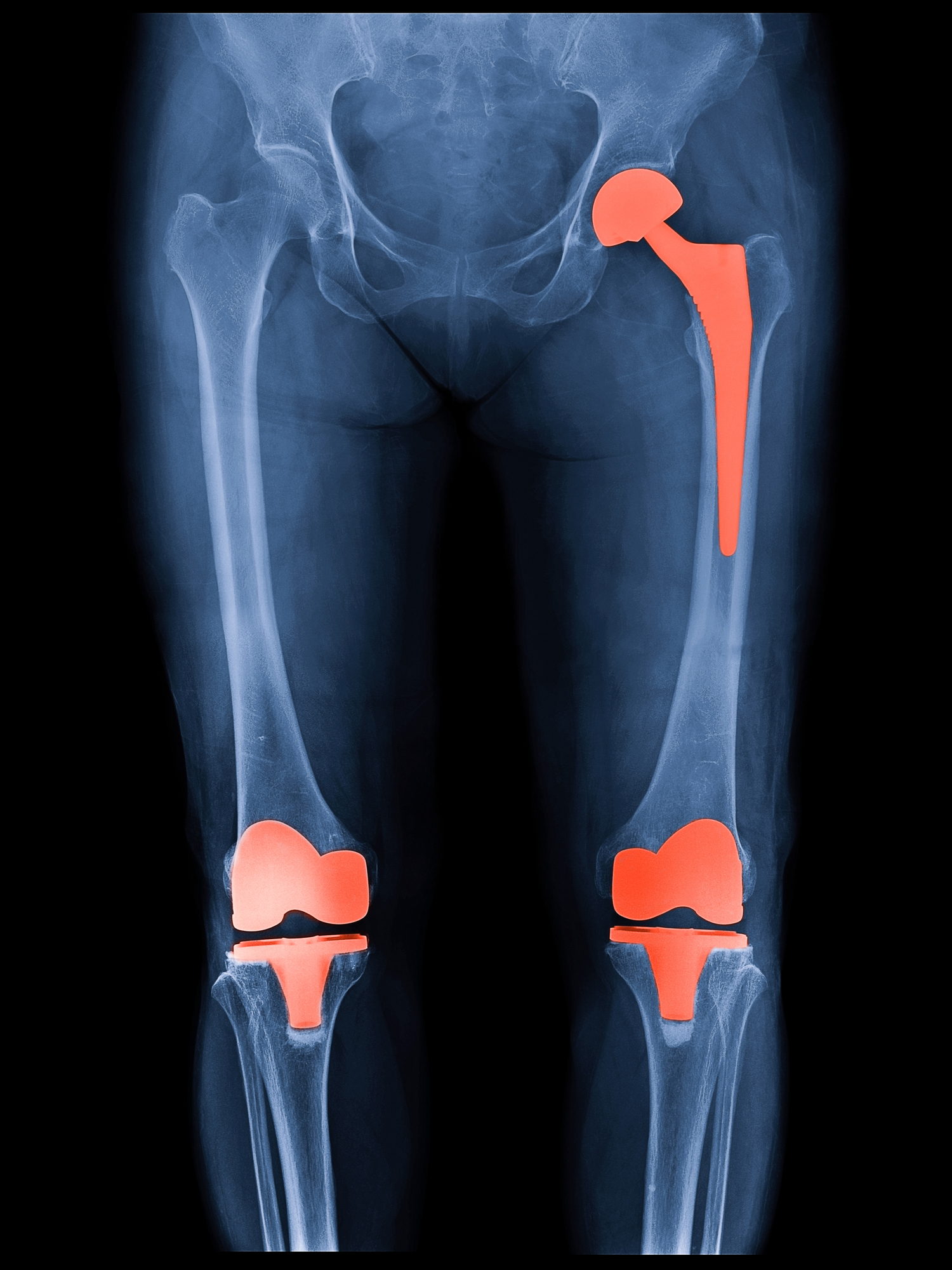
Is obesity a reason to avoid joint replacement surgery? - Harvard Health Blog - Harvard Health Publishing
How Much Does Hip Replacement Cost?
Medicare and hip replacement: Coverage, eligibility, and costs
Cost of Surgical Treatment for Distal Radius Fractures and the Implications of Episode-Based Bundled Payments - Journal of Hand Surgery
Avoid These Big Medicare Mistakes People Make
Optimal Hospital and Surgeon Volume Thresholds to Improve 30-Day Readmission Rates, Costs, and Length of Stay for Total Hip Replacement - The Journal of Arthroplasty
Risk factors associated with revision for prosthetic joint infection after hip replacement: a prospective observational cohort study - The Lancet Infectious Diseases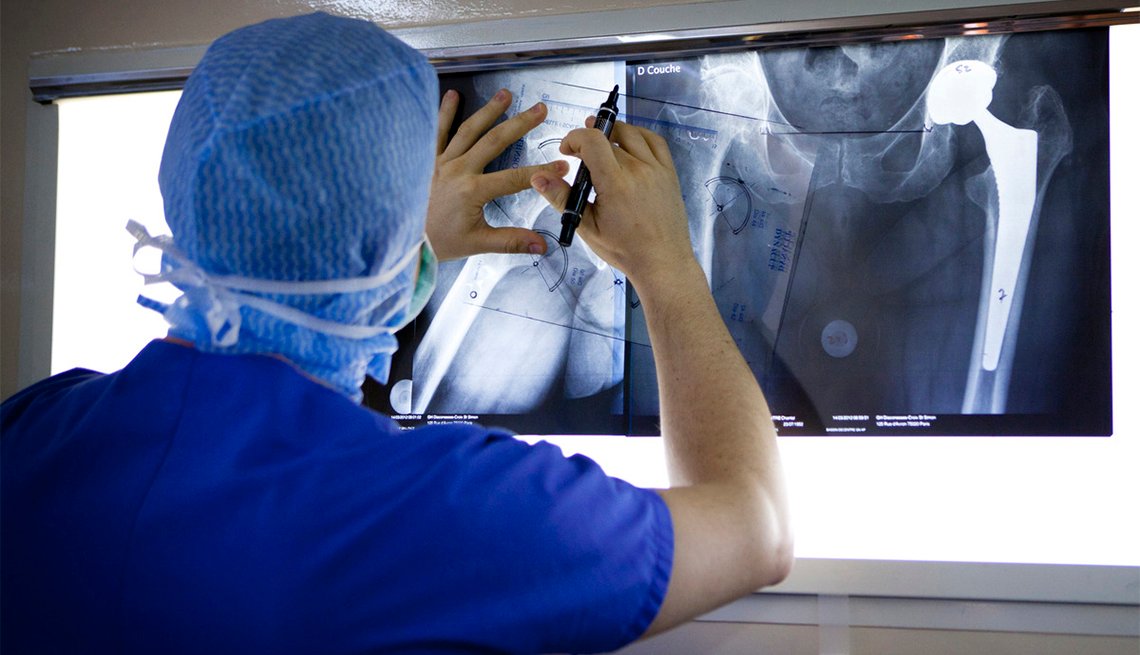
The Benefits of Outpatient Hip Replacement Surgery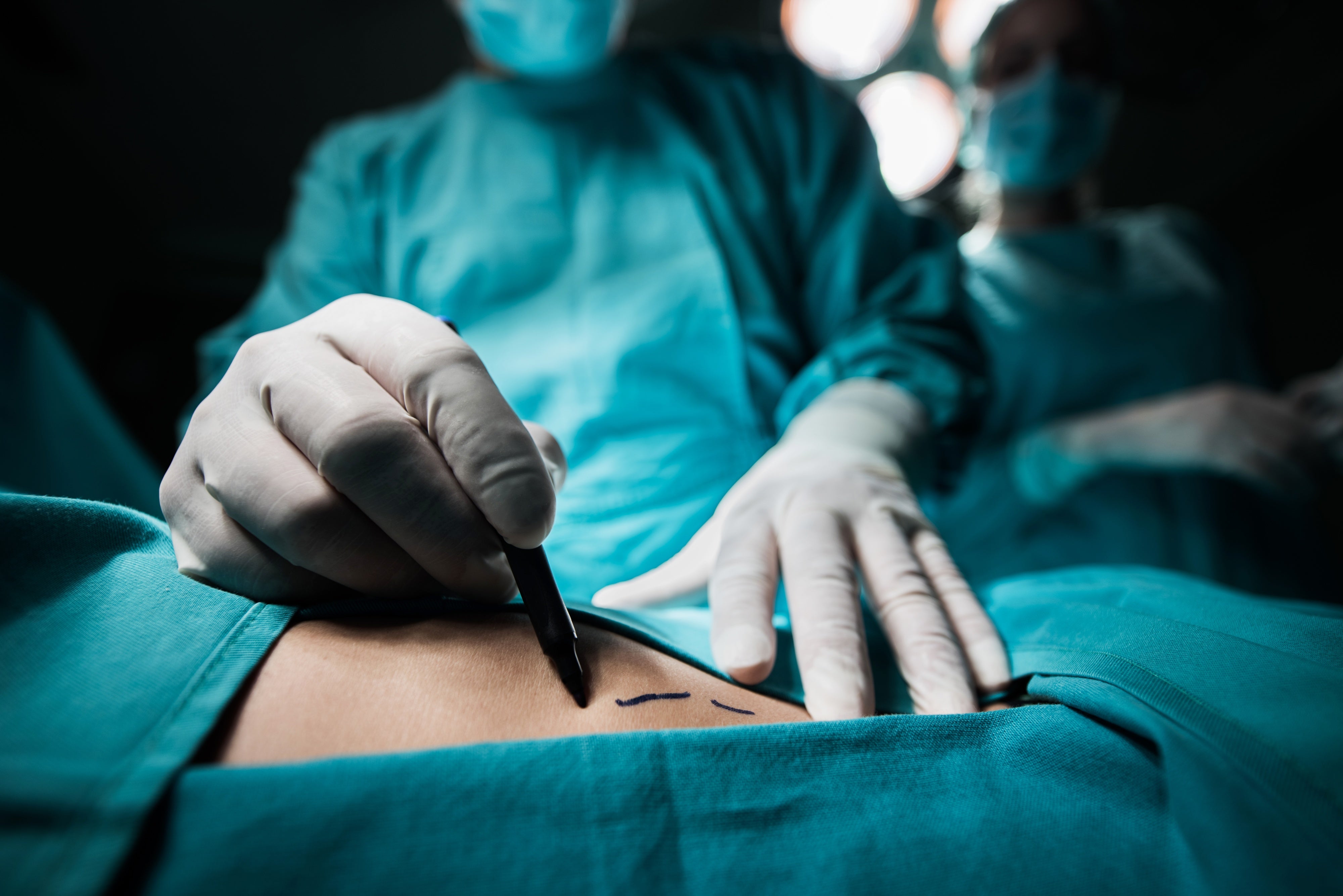
Surgery Near End of Life Is Common, Costly - Scientific American
 Scary Truth: Does Medicare Cover Hip Replacement Surgery?
Scary Truth: Does Medicare Cover Hip Replacement Surgery?






















/considering-hip-replacement-surgery-2549565-v11-3d3b7eafd288402d87af34c275996f26.png)













Posting Komentar untuk "cost of hip replacement surgery with medicare"